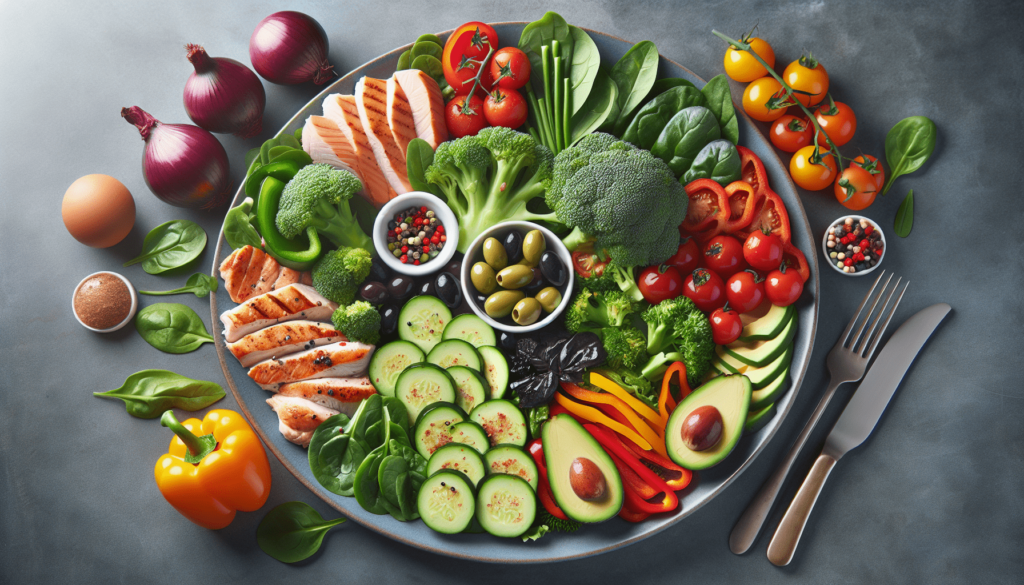
Are you looking for an effective way to lose weight and improve your overall health? Look no further than the Keto Diet Eating Plan. This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of what the keto diet entails and how it can benefit you. By following this low-carb, high-fat eating plan, you can achieve ketosis, a metabolic state that helps your body burn fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. Get ready to embark on a new and fulfilling journey towards a healthier you with the Keto Diet Eating Plan.
What is the Keto Diet?
Definition of the Keto Diet
The Keto Diet, also known as the ketogenic diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that has gained popularity in recent years. This diet involves reducing your intake of carbs while increasing your consumption of fats. By doing so, your body enters a state called ketosis, where it starts using stored fat as its primary fuel source instead of carbohydrates.
Purpose of the Keto Diet
The main purpose of the Keto Diet is to induce ketosis and shift your body’s metabolism from using glucose as an energy source to using ketones. This metabolic shift can promote weight loss, regulate blood sugar levels, and improve overall health. Additionally, the Keto Diet has been used for decades as a therapeutic approach for managing epilepsy in children.
How the Keto Diet Works
The Keto Diet works by drastically reducing your carb intake, typically to less than 50 grams per day. When your carb intake is limited, your body depletes its glycogen stores and turns to fat for energy. This fat is broken down into ketones in the liver, which are then used to fuel your body and brain. By entering a state of ketosis, your body becomes more efficient at burning fat and can lead to weight loss.
Benefits and Risks of the Keto Diet
The Keto Diet has various benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, reduced appetite, increased mental clarity, and a potential reduction in inflammation. Some studies also suggest that the Keto Diet may help manage certain medical conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and epilepsy.
However, it is important to note that the Keto Diet is not suitable for everyone, and there are potential risks involved. The initial transition into ketosis may cause side effects known as the “keto flu,” which can include fatigue, headache, and nausea. Additionally, the high-fat content of the diet may increase the risk of heart disease in some individuals. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting the Keto Diet to determine if it is suitable for you.
Creating a Keto Diet Eating Plan
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the three main components of your diet: carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Understanding how these macronutrients contribute to your overall diet is essential when creating a Keto Diet eating plan. On the Keto Diet, the goal is to consume around 70-75% of calories from fat, 20-25% from protein, and 5-10% from carbohydrates.
Determining Daily Caloric Intake
To create a Keto Diet eating plan, it is important to determine your daily caloric intake. This can be calculated using various online calculators or by consulting a registered dietitian. Factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level should be taken into consideration when calculating your caloric needs.
Setting Macro Goals
Once you have determined your daily caloric intake, you can set macro goals based on the recommended macronutrient ratios for the Keto Diet. This involves calculating the grams of fat, protein, and carbs you should aim for each day. For example, if your daily caloric intake is 2000 calories, you would aim for approximately 150 grams of fat, 100 grams of protein, and 25 grams of carbohydrates.
Foods to Include in a Keto Diet
A Keto Diet should primarily focus on foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats. Some foods that are suitable for a Keto Diet include:
- Low-carb vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and bell peppers.
- Meat and poultry: Beef, chicken, turkey, and lamb.
- Fish and seafood: Salmon, tuna, shrimp, and mackerel.
- Healthy fats: Avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, and butter.
- Dairy products: Cheese, butter, cream, and full-fat yogurt.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries.
- Herbs and spices: Turmeric, basil, oregano, and cinnamon.
Foods to Avoid in a Keto Diet
On the Keto Diet, it is important to avoid foods that are high in carbohydrates and sugar. Some foods to avoid include:
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, corn, peas, and butternut squash.
- Grains and cereals: Wheat, rice, oats, and cereal.
- Sugary foods and sweets: Candy, soda, ice cream, and desserts.
- Processed and fast foods: Chips, cookies, fast food burgers, and french fries.
- Trans fats and vegetable oils: Margarine, vegetable oil, and canola oil.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Meal planning and preparation are crucial for success on a Keto Diet. Planning your meals in advance can help ensure that you have the necessary ingredients on hand and prevent you from making impulsive food choices. Preparing meals in bulk and portioning them out can also save time and make it easier to stick to your Keto Diet. Additionally, having keto-friendly snacks available can prevent you from reaching for non-compliant foods when hunger strikes. Tracking and monitoring your food intake using smartphone apps or food journals can help you stay on track and make adjustments if needed.
Understanding Macronutrients
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients and serve as the body’s primary source of energy. In the Keto Diet, carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced to induce ketosis. This means that foods high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and rice, should be limited or avoided. Instead, low-carb vegetables and small amounts of berries should be consumed.
Protein
Protein is essential for tissue repair, muscle growth, and various metabolic functions. On the Keto Diet, protein intake should be moderate, accounting for about 20-25% of your daily caloric intake. Good sources of protein include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. It is important to choose high-quality protein sources and avoid processed or breaded meats.
Fats
Fats are the primary source of fuel on the Keto Diet, providing energy and promoting satiety. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, should be emphasized. Saturated fats, which are found in coconut oil and butter, can also be included in moderation. However, it is important to limit the consumption of trans fats and vegetable oils, as they can increase the risk of heart disease.
Determining Daily Caloric Intake
Caloric Needs Calculation
Determining your daily caloric intake is essential in creating a Keto Diet eating plan. To calculate your approximate caloric needs, various formulas take into account factors such as age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. Consulting a registered dietitian or using online calculators can provide you with an estimate of your daily caloric needs.
Factors to Consider
When calculating your daily caloric intake for the Keto Diet, there are additional factors to consider. These include your goals, overall health, and any medical conditions you may have. If you are looking to lose weight, a calorie deficit may be necessary. However, it is important to be mindful of your body’s needs and ensure you are getting enough nutrients for optimal health.

Setting Macro Goals
Calculating Macronutrient Ratios
Setting macro goals involves determining the specific grams of fat, protein, and carbohydrates you should consume daily. These macronutrient ratios are typically followed on the Keto Diet:
- Fat: 70-75% of total calories
- Protein: 20-25% of total calories
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of total calories
To calculate your macro goals, you can use your daily caloric intake and the recommended percentages. For example, if your daily caloric intake is 2000 calories, your macro goals would be approximately 150 grams of fat, 100 grams of protein, and 25 grams of carbohydrates.
Adjusting Ratios for Individual Needs
It is important to note that the recommended macronutrient ratios may need to be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences. Some individuals may find that they tolerate slightly higher or lower carbohydrate intake while still maintaining ketosis. Experimenting with different ratios and monitoring the effects on your body can help you determine the optimal macro goals for your specific needs.
Foods to Include in a Keto Diet
Low-Carb Vegetables
Low-carb vegetables are a staple of the Keto Diet, as they provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber while containing minimal carbohydrates. Some examples of low-carb vegetables include leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce), cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts), and zucchini. These vegetables can be enjoyed in salads, stir-fries, or as side dishes.
Meat and Poultry
Meat and poultry are excellent sources of protein and healthy fats on the Keto Diet. Opt for grass-fed, organic, or pasture-raised meat whenever possible, as it tends to be higher in beneficial nutrients. Good choices include beef, chicken, turkey, pork, and lamb. It is important to avoid processed or breaded meats, as they often contain added sugars or fillers.
Fish and Seafood
Fish and seafood are not only rich in protein but also provide essential omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are particularly beneficial. These seafood options can be grilled, baked, or pan-seared to create delicious keto-friendly meals. Avoid breading or high-carb sauces when preparing fish and seafood.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are a crucial part of the Keto Diet, as they provide energy and help you feel satiated. Incorporate foods high in healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and butter, into your meals. These fats can be used for cooking, dressing salads, or added to smoothies. It is important to consume fats in moderation and not exceed your daily caloric goals.
Dairy Products
Dairy products can be included in a Keto Diet, but it is important to choose full-fat options and be mindful of their carb content. Good dairy choices include cheese, butter, cream, and full-fat yogurt. However, individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies should avoid these products or opt for lactose-free alternatives.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are a convenient and portable snack option on the Keto Diet. They provide healthy fats, protein, and fiber. Good choices include almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. However, it is important to moderate your intake, as nuts and seeds can be high in calories. Stick to a handful of nuts or a tablespoon of seeds as a serving size.
Berries
While fruits are generally limited on the Keto Diet due to their high sugar content, some berries can be enjoyed in moderation. Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are relatively low in carbs and can add natural sweetness to your meals or snacks. Remember to account for their carbohydrate content when tracking your daily intake.
Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices can enhance the flavor of your dishes while adding virtually no calories or carbohydrates. Incorporate herbs like basil, oregano, cilantro, and rosemary into your cooking. Spices such as turmeric, cayenne pepper, cinnamon, and ginger can add a kick of flavor. Experiment with different combinations to create delicious and satisfying Keto Diet meals.
Foods to Avoid in a Keto Diet
Starchy Vegetables
Starchy vegetables should be avoided on the Keto Diet due to their high carbohydrate content. Examples of starchy vegetables include potatoes, corn, peas, and butternut squash. These vegetables can significantly impact your daily carb intake and make it challenging to maintain ketosis. Instead, opt for non-starchy vegetables with fewer carbs and more fiber.
Grains and Cereals
Grains and cereals are high in carbohydrates and should be avoided on the Keto Diet. This includes wheat, rice, oats, barley, and all products made from these grains, such as bread, pasta, and cereal. Instead of these carb-heavy options, focus on incorporating low-carb alternatives like cauliflower rice or zucchini noodles.
Sugary Foods and Sweets
Sugary foods and sweets are obvious candidates to avoid on the Keto Diet. Candy, soda, ice cream, cookies, cakes, and other high-sugar treats should be strictly limited or eliminated altogether. These foods can cause blood sugar spikes and hinder your progress towards ketosis and weight loss. Instead, satisfy your sweet tooth with keto-friendly desserts made with natural sweeteners like stevia or erythritol.
Processed and Fast Foods
Processed and fast foods are typically high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and hidden carbohydrates. Foods like chips, cookies, fast food burgers, and french fries should be avoided on the Keto Diet. These foods not only hinder weight loss but can also negatively impact your overall health. Instead, prioritize whole, unprocessed foods that are nutrient-dense.
Trans Fats and Vegetable Oils
Trans fats and vegetable oils should be avoided on the Keto Diet due to their detrimental effects on heart health. These fats are commonly found in margarine, vegetable oil, canola oil, and many processed and fried foods. Instead, opt for healthier fat options like avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, and grass-fed butter.
Meal Planning and Preparation
Weekly Meal Planning
Meal planning is a crucial step in successfully following the Keto Diet. Taking the time to plan your meals in advance can make grocery shopping easier and prevent you from making impulsive food choices. Start by creating a weekly meal plan that includes a variety of keto-friendly recipes and ingredients. This can help you stay on track and ensure you have all the necessary items on hand.
Prepping Meals in Advance
Meal prepping is a time-saving strategy that can make it easier to stick to your Keto Diet eating plan. By preparing meals in advance, you can avoid the temptation of reaching for unhealthy options when you are short on time or energy. Cook and portion out your meals for the week, storing them in individual containers for easy grab-and-go options. This can also help with portion control and monitoring your macronutrient ratios.
Keto-friendly Snack Options
Having keto-friendly snacks readily available can help you stay on track and prevent cravings for non-compliant foods. Some keto-friendly snack options include nuts, seeds, cheese, hard-boiled eggs, sliced avocado, and beef jerky. Keeping these snacks on hand at home, work, or while traveling can ensure you always have a healthy option to satisfy your hunger.
Eating Out on a Keto Diet
While eating out on the Keto Diet can be challenging, it is still possible to make keto-friendly choices. Most restaurants offer meat or seafood options that can be paired with non-starchy vegetables. Avoid sauces and dressings that may contain added sugars or high-carb thickeners. Opt for olive oil and vinegar or ask for condiments on the side to control your intake. Additionally, be mindful of portion sizes and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Tracking and Monitoring
Tracking and monitoring your food intake is essential to ensure you are staying within your macro goals and maintaining ketosis. Smartphone apps or food journals can help you keep a record of what you eat and track the nutritional content of your meals. By monitoring your progress and making adjustments as needed, you can fine-tune your Keto Diet eating plan and maximize its effectiveness.

Tips for Success on a Keto Diet
Gradual Transition
Transitioning to a Keto Diet can be challenging, especially if you are used to a high-carb diet. Gradually reducing your carbohydrate intake over a few weeks can ease the transition and minimize potential side effects. Start by cutting out processed and sugary foods, then gradually decrease your carbohydrate intake while increasing your healthy fat consumption. This gradual approach can help your body adapt to using fat as its primary fuel source.
Hydration Importance
Proper hydration is crucial on the Keto Diet. As your body transitions into ketosis, it excretes more water and electrolytes, which can lead to dehydration if not properly replenished. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day and consider adding electrolyte-rich drinks or supplements to your routine. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, can help prevent the “keto flu” and maintain overall hydration.
Supplement Considerations
While the Keto Diet can provide many essential nutrients, there are certain vitamins and minerals that may need to be supplemented. These include vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and certain B vitamins. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine if you have any nutrient deficiencies and to discuss appropriate supplementation.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can enhance the effects of the Keto Diet. Exercise can help boost weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall well-being. Engage in a combination of cardiovascular exercise and strength training to maximize the benefits. It is important to listen to your body and adjust your exercise intensity as needed, especially during the transition phase.
Staying Motivated and Accountable
Staying motivated and accountable is key to long-term success on the Keto Diet. Find a support system, whether it be friends, family, or online communities, to keep you motivated and provide guidance along the way. Set realistic goals and celebrate your achievements, whether it is weight loss, improved energy levels, or better overall health. Taking progress photos or keeping a journal can also help you stay committed and track your journey.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Keto Flu
The transition into ketosis can cause side effects known as the “keto flu.” These symptoms can include fatigue, headache, dizziness, irritability, and nausea. They typically subside within a week or two as your body adjusts to using ketones for energy. Staying properly hydrated, replenishing electrolytes, and getting plenty of rest can help minimize the discomfort.
Electrolyte Imbalance
As mentioned earlier, the Keto Diet can cause an increased excretion of water and electrolytes. This can lead to an imbalance of sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which are essential for proper bodily functions. To prevent this imbalance, consider adding electrolyte-rich foods or supplements to your diet. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate supplementation for your individual needs.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some individuals may experience digestive issues when starting the Keto Diet. This can include constipation, diarrhea, or changes in bowel movements. To prevent or manage these symptoms, focus on consuming plenty of fiber from low-carb vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Drinking enough water and staying hydrated can also help keep your digestive system running smoothly.
Individual Health Considerations
Individual health considerations should be taken into account before starting the Keto Diet. If you have any pre-existing medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine if the Keto Diet is suitable for you. Additionally, pregnant or breastfeeding women should approach the Keto Diet with caution, as it may not provide sufficient nutrients for both the mother and the baby.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
Before embarking on any dietary changes, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They can assess your specific health needs and help create a personalized Keto Diet eating plan that aligns with your goals and overall well-being. They can also monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed to ensure you are on the right track.
In conclusion, the Keto Diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that aims to induce ketosis and shift the body’s metabolism to burn fat for fuel. It has been shown to promote weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and potentially benefit certain medical conditions. Understanding macronutrients, determining daily caloric intake, setting macro goals, and planning and preparing meals are important aspects of creating a successful Keto Diet eating plan. By including low-carb vegetables, healthy fats, and quality sources of protein, while avoiding high-carb foods and processed products, you can enjoy the benefits of the Keto Diet. However, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and precautions, and to consult with a healthcare professional before starting this or any new diet. With proper planning, monitoring, and support, the Keto Diet can be a viable option for individuals seeking weight loss or improved health.